1. Common Applications (What Cars/Trucks Use It?)
This pump is famously associated with several iconic diesel engines, primarily from Volkswagen and Audi. The most common application is the 1.9L TDI (Turbocharged Direct Injection) engine.
Primary Vehicles:
Volkswagen Golf Mk3 (1993-1998)
Volkswagen Jetta Mk3 (1993-1998)
Volkswagen Passat B4 (1995-1997)
Audi A4 B5 (1996-1997)
Volkswagen Eurovan (1992-1999)
Engines it was fitted to:
⚠️ Important Note: While it's most famous for the 1.9L TDI, this pump number was used on other engines as well. Always confirm the exact part number on your old pump and cross-reference it with your vehicle's VIN.
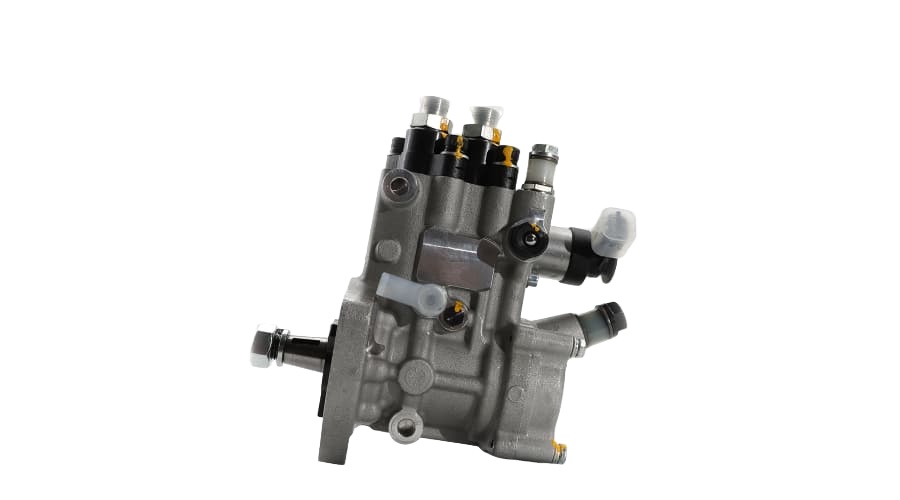
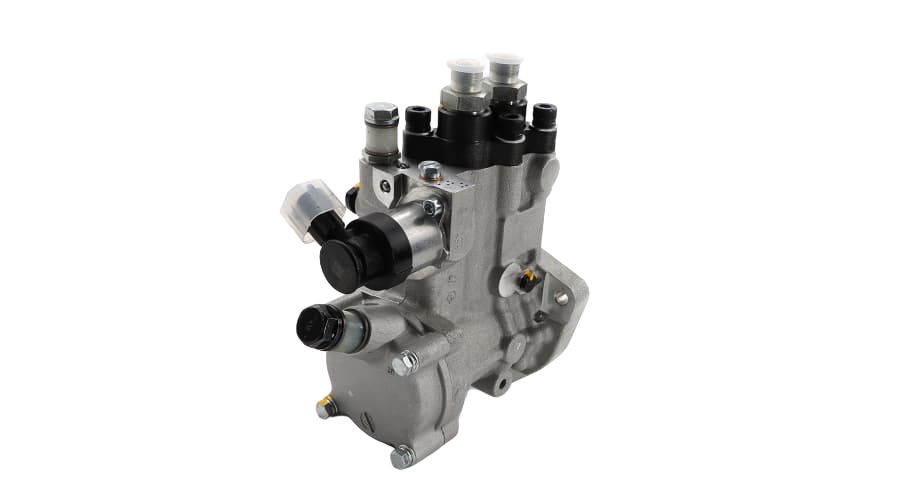
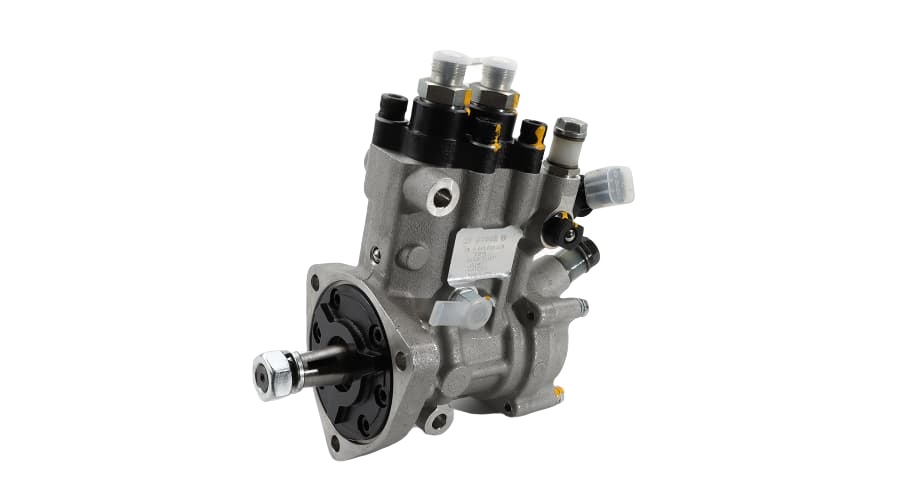
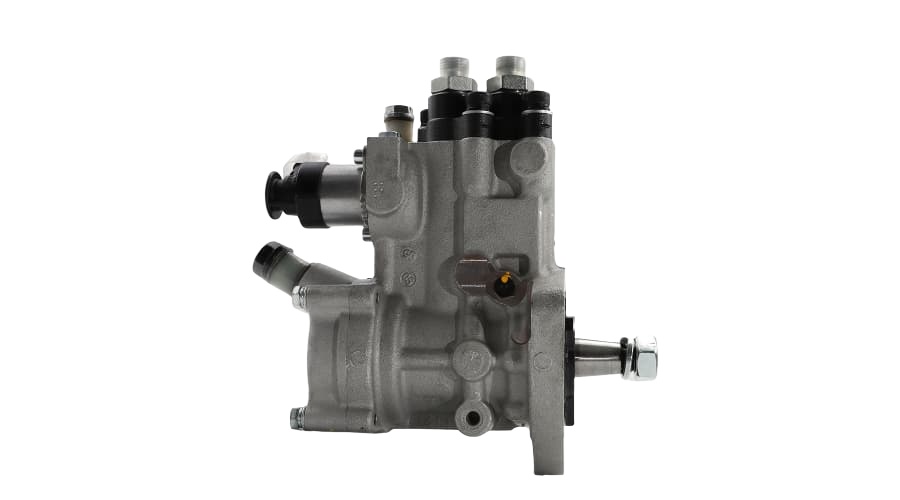
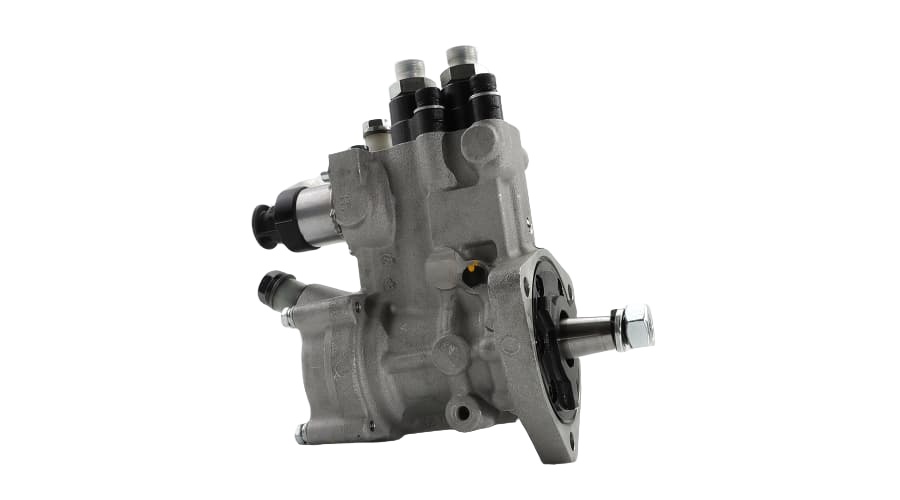
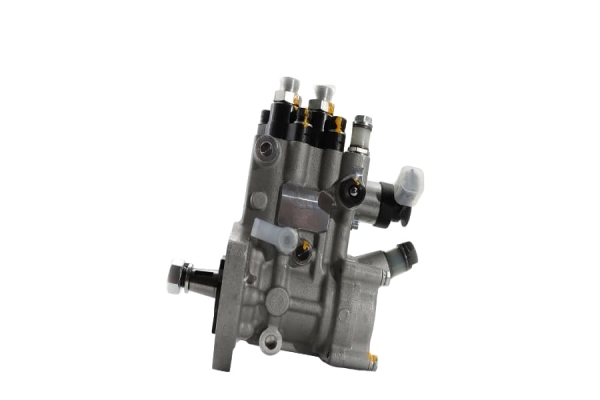
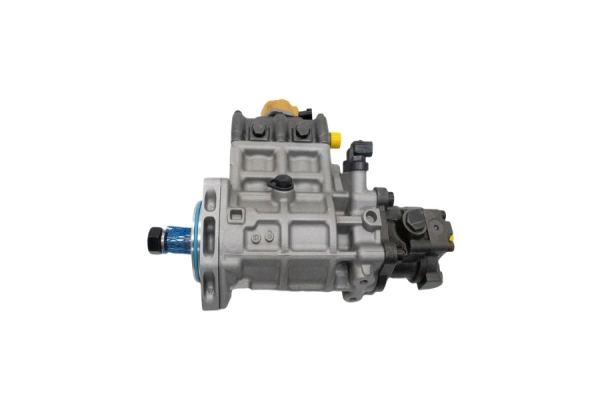
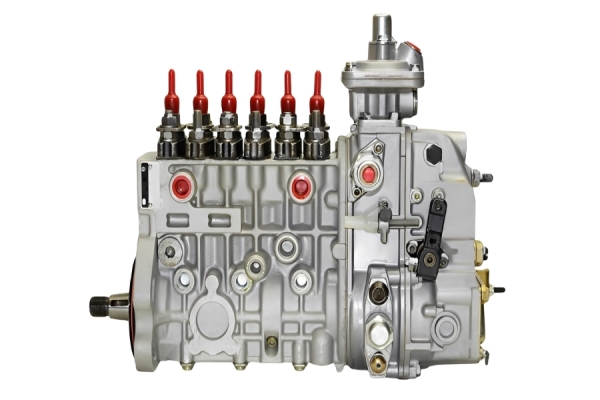
2. Key Features of the VE Pump
Mechanical Operation: It uses a single plunger (distributor head) to meter and distribute fuel to each injector at high pressure. It's driven by the engine's timing belt.
Integrated Governor: Has a mechanical governor to control the maximum and idle speeds of the engine.
LDA (Load-Dependent Aneroid): This is a boost-pressure-controlled device that increases fuel delivery as turbocharger boost increases, improving performance and reducing smoke.
Cold Start Advance: An automatic advance mechanism for easier cold starting.
Fuel Cut-Off Solenoid: An electrically controlled solenoid that shuts off fuel to the injectors when the ignition is turned off, stopping the engine.
3. Common Problems & Symptoms
The VE pump is generally very robust, but it can develop issues, especially with age and mileage.
Common Failure Points:
Head Seal / Top Seal Failure: The most common leak. You'll see diesel fuel pooling on the top of the pump. The seals harden over time.
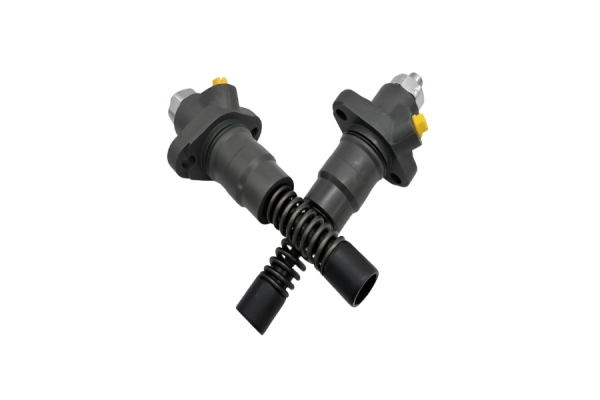
Quantity Adjuster (QA) Failure: The QA is an electro-mechanical unit inside the pump that controls fuel quantity. When it fails, it can cause:
Fuel Cut-Off Solenoid Failure: If this fails, the engine will not start as no fuel can reach the injectors.
LDA Diaphragm Failure: Can cause excessive black smoke under acceleration and a lack of power.
Worn Pump Head/Plunger: Internal wear from contaminated fuel or lack of lubrication leads to low injection pressure, resulting in hard starting, rough idle, and loss of power.
Typical Symptoms of a Failing Pump:
Hard Starting, especially when the engine is warm.
Loss of Power and poor acceleration.
Rough Idle or erratic engine speed.
Excessive Black Smoke from the exhaust.
Diesel Fuel Leaks from the pump body.
Increased Fuel Consumption.
Engine Stalling.
4. What to Do If You Need One
Diagnosis First: Don't just assume the pump is bad. Many symptoms can be caused by clogged fuel filters, faulty injectors, or vacuum leaks (for the LDA). Have a qualified diesel mechanic diagnose the issue.
Rebuild vs. Replace:
Rebuilding: A specialist can rebuild your existing pump with new seals, calibrated and tested. This is often the most cost-effective and reliable option.
Used Pump: Can be a gamble unless it's tested and guaranteed.
New/Remanufactured Pump: The best but most expensive option. Companies like Bosch offer certified remanufactured units.
Timing is Critical: When replacing or reinstalling the pump, the engine's injection pump timing must be set precisely using a diagnostic scanner (like VCDS for VWs) to read "TDI Timing" in the basic settings. Incorrect timing can cause poor performance, overheating, and engine damage.
Summary
The Bosch 0445025029 is a legendary and reliable diesel injection pump found on millions of 1990s VW and Audi TDI vehicles. If you own one of these cars and are experiencing diesel-related issues, this pump is a key component to check. Due to its complexity, work on it is best left to experienced diesel injection specialists.
If you are looking to buy one, be sure you are getting the correct part for your specific engine code.