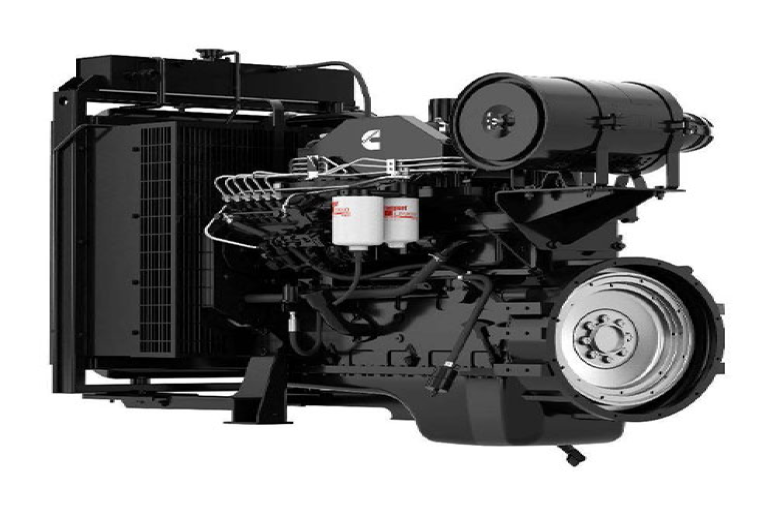
How much do you know about the internal structure and daily maintenance of Cummins' 6BT5.9 engine ?
The Cummins 6BT5.9 engine is a widely used diesel engine known for its reliability and durability. Below is a detailed breakdown of its diesel system components, functions, applications, common problems, and maintenance suggestions.
1. Main Components & Functions of the Diesel System
The diesel system in the 6BT5.9 consists of several key components:
Fuel Supply System
Fuel Tank – Stores diesel fuel.
Fuel Transfer Pump (Lift Pump) – Draws fuel from the tank and supplies it to the injection pump.
Fuel Filters (Primary & Secondary) – Remove contaminants to protect the injection system.
Primary filter (water separator) removes water and large particles.
Secondary filter (fine filtration) ensures clean fuel reaches the injectors.
Injection Pump (Rotary or Inline) – Pressurizes and delivers fuel to the injectors at precise timings.
Common models: Bosch VE rotary pump or Bosch P7100 inline pump.
Fuel Injectors – Atomize fuel into the combustion chamber.
Fuel Return Line – Returns excess fuel to the tank.
Air Intake & Turbocharging (if equipped)
Turbocharger (optional, in some models) – Increases air intake for better combustion efficiency.
Intercooler (if turbocharged) – Cools compressed air for denser intake.
Governor & Control System
Mechanical or electronic governor regulates engine speed.
2. Main Application Scenarios & Equipment Models
The 6BT5.9 is used in a variety of industries due to its 135–230 HP power range and 5.9L displacement.
Common Applications:
Trucks & Commercial Vehicles
Dodge Ram (1st Gen Cummins, 1989–1993)
Freightliner, International trucks
Construction & Agricultural Equipment
Bobcat skid steers, Case backhoes
John Deere tractors
Marine Engines
Small boats, work vessels
Generators & Industrial Power Units
Used in standby and prime power gensets
Military & Emergency Vehicles
Humvees, fire trucks
3. Common Problems & Maintenance Suggestions
Despite its reliability, the 6BT5.9 has some recurring issues:
A. Fuel System Problems
Clogged Fuel Filters
Symptoms: Hard starting, power loss, rough idle.
Solution: Replace filters every 10,000–15,000 miles (or per OEM recommendation).
Air in Fuel System
Symptoms: Engine stalling, difficulty starting.
Solution: Bleed the system by loosening injector lines and cranking until fuel flows cleanly.
Injector Failure
Symptoms: Excessive smoke (black/white), misfires.
Solution: Test injectors, replace if leaking or clogged.
Injection Pump Wear (VE Rotary Pump Issues)
Symptoms: Loss of power, erratic RPM, hard cold starts.
Solution: Rebuild or replace the pump; avoid low-quality diesel.
B. Turbocharger Issues (If Equipped)
Oil Leaks / Turbo Failure
Symptoms: Blue smoke, whining noise, power loss.
Solution: Check oil supply, replace seals or turbo if damaged.
C. Cooling System Problems
Overheating
Causes: Clogged radiator, faulty thermostat, water pump failure.
Solution: Flush coolant system, replace worn components.
D. Oil Leaks (Common Areas)
Rear Main Seal, Valve Cover Gasket, Front Crankshaft Seal
Solution: Replace seals with high-quality parts.
E. KDP (Killer Dowel Pin) Issue (Early Models)
Problem: The front gear train dowel pin can work loose and damage the timing gear.
Solution: Inspect and secure the pin (aftermarket kits available).
4. Maintenance Recommendations
Regular Oil Changes – Every 5,000–7,500 miles (use 15W-40 diesel oil).
Fuel Filter Replacement – Every 10,000–15,000 miles.
Coolant Flush – Every 2–3 years (use extended-life coolant).
Injector & Pump Service – Inspect every 50,000 miles.
Turbo Maintenance – Check for shaft play, ensure proper oil supply.
Conclusion
The Cummins 6BT5.9 is a robust engine widely used in trucks, construction equipment, and generators. Fuel system maintenance, turbo care, and leak prevention are key to longevity. Addressing common issues like clogged filters, injector problems, and KDP risks will ensure reliable performance for years.
