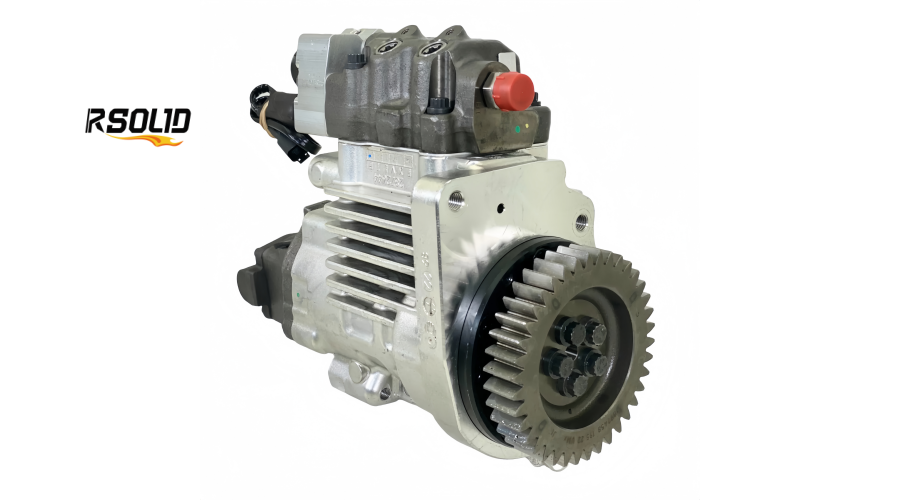
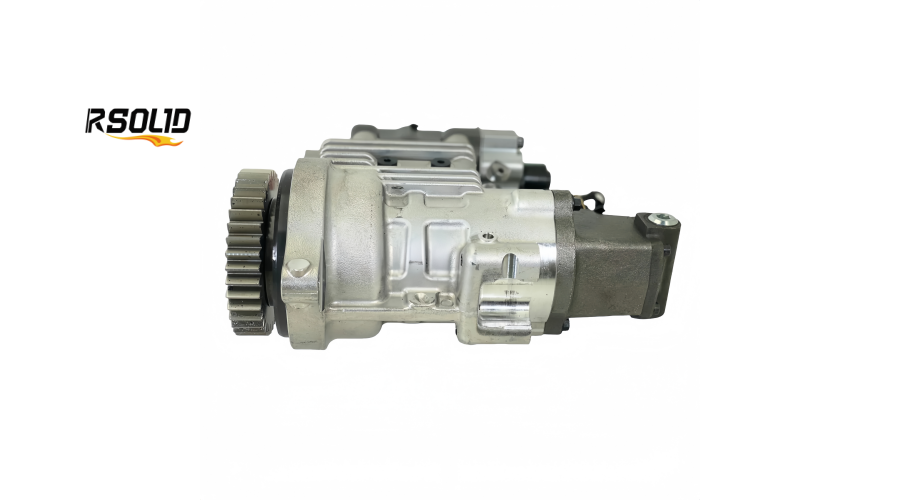
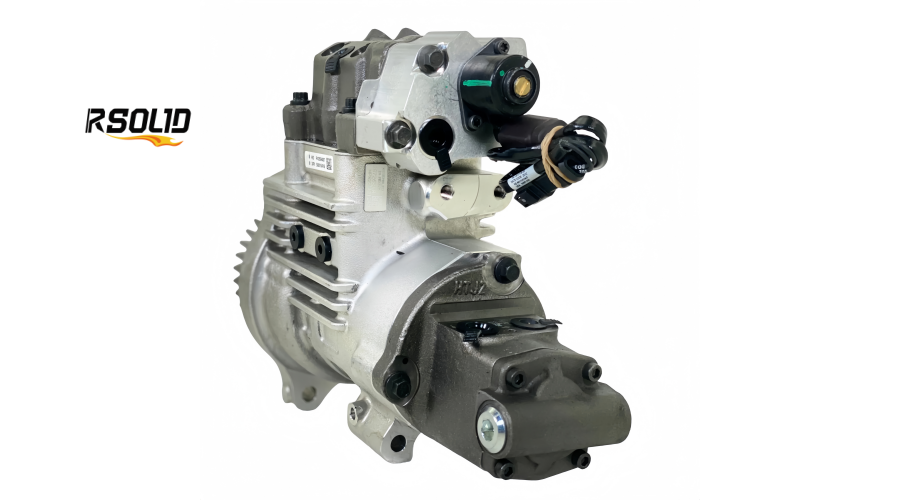
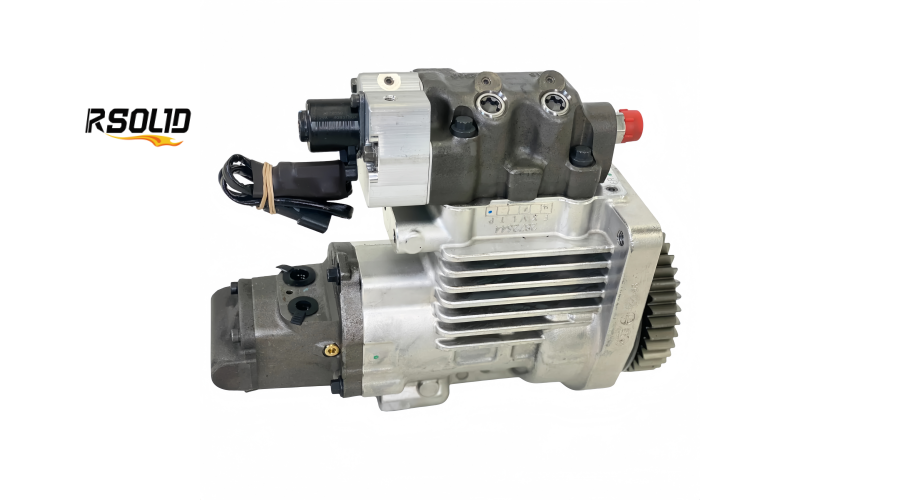
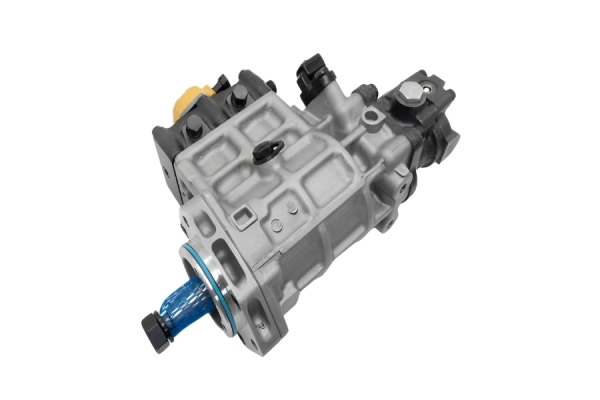
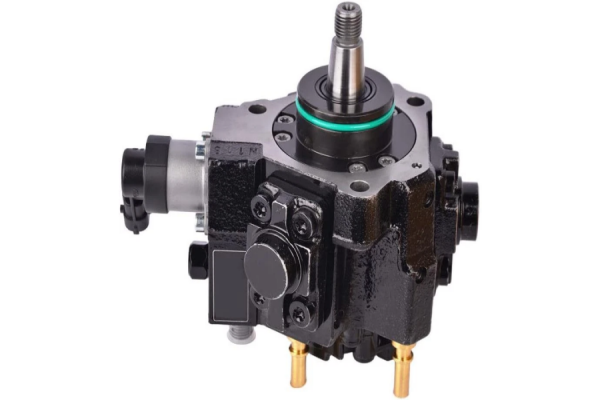
Eliminates a Separate Transfer Pump: This simplifies the fuel system architecture, reducing potential leak points and parts.
Positive Priming & Supply: It ensures a steady, high-volume supply of filtered fuel to the high-pressure section, preventing cavitation—a critical requirement for the next stage.
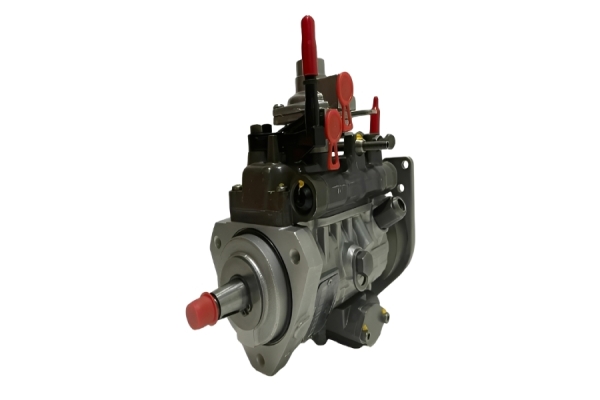
2. Radial Piston Design (Multiple Pistons)
Structure: Unlike the single or dual piston plunger pumps of previous systems, this HPFP uses multiple radial pistons (typically three or four) arranged like a star around the central cam.
Advantages:
Smoother Flow & Pressure: Multiple pistons create overlapping pressure pulses, leading to significantly more consistent high-pressure fuel delivery to the common rail, with less ripple. This is crucial for precise injector control.
Higher Volumetric Efficiency: It can move more fuel per revolution, enabling it to supply enough volume at the extreme pressures needed for clean combustion under all load conditions.
Reduced Vibration & Stress: The multi-piston design inherently balances forces better than single-piston designs, reducing vibration and component stress.
3. Hardened Steel Construction & Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) Coatings
Structure: Critical components like the pistons, cam ring, and bore are made from ultra-hard, precision-ground steels. The pistons and rollers are often coated with a Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) coating.
Advantages:
Extreme Pressure Resistance: Withstands the incredible internal forces of 35,000 psi operation.
Exceptional Wear Resistance: The DLC coating is one of the hardest, slickest surfaces available. It drastically reduces friction and wear between the piston foot and its roller, and the piston and its bore—the two highest-wear interfaces in the pump.
Longevity Under Contamination: While fuel contamination is still the enemy, these hardened materials are more resilient to minor particulate abrasion than older designs.
4. Integral Pressure Relief & Regulation Valves
Structure: Advanced solenoid-controlled metering and pressure relief valves are built directly into the pump housing.
Advantage:
ECM-Controlled Precision: The Engine Control Module (ECM) can precisely modulate the pump's output in real-time. By controlling the metering valve, it regulates how much fuel enters the high-pressure chamber, allowing for on-demand pressure generation. This improves efficiency and reduces parasitic load compared to pumps that constantly generate maximum pressure.
5. Compact, Rigid Housing Design
Structure: The entire assembly is housed in a single, robust aluminum or cast-iron casing that mounts directly to the engine gear housing.
Advantages:
Direct Gear Drive: It is driven by the engine's gear train, ensuring positive timing and eliminating the slippage or wear issues possible with belt or chain drives.
Structural Integrity: The rigid housing maintains perfect alignment of the cam, pistons, and bores under severe thermal and mechanical loads.
Effective Lubrication & Cooling: Engine oil is circulated through dedicated passages in the pump housing to lubricate the cam, rollers, and bearings, and to help cool the unit.